
6 However, PV isolation is not frequently performed in this patients’ population as it is still unclear whether PV triggering is the underlying pathophysiological mechanism of AF in BS. Pulmonary vein (PV) isolation is nowadays the cornerstone of percutaneous transcatheter ablation for drug-resistant paroxysmal AF.

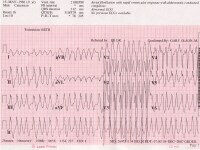
Moreover, patients with BS and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) might experience inappropriate shocks due to AF with rapid ventricular response. 2–5 Pharmacological treatment of AF in the setting of BS might be challenging as many antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) with sodium channel blocking properties might lead to to the development of ventricular arrhythmias. 1 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common supraventricular arrhythmia in patients with BS, with a reported prevalence of 3–20%. No major complications occurred in the study population.īrugada syndrome (BS) is characterized by a distinct electrocardiographic pattern consisting of a right bundle branch block-like morphology and ST elevation in the right precordial leads in patients without structural heart disease carrying the risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD) due to malignant ventricular arrhythmias. Patients with inappropriate ICD interventions due to AF did not present futher ICD shocks after catheter ablation.

The freedom from recurrence of atrial fibrillation was 74% during a 3-year follow up and without antiarrhythmic drugs. The present study analysed the largest population of patients with Brugada syndrome and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation treated with catheter ablation over a long-term follow up.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
